前面介绍bean加载时都是站在BeanFactory的角度上进行的,相当于将spring纯粹当成一个bean容器工具来使用。其实spring另外提供了一套接口ApplicationContext,更加侧重于将BeanFactory放在一个上下文中来使用,这样方便在其基础上做一些扩展。
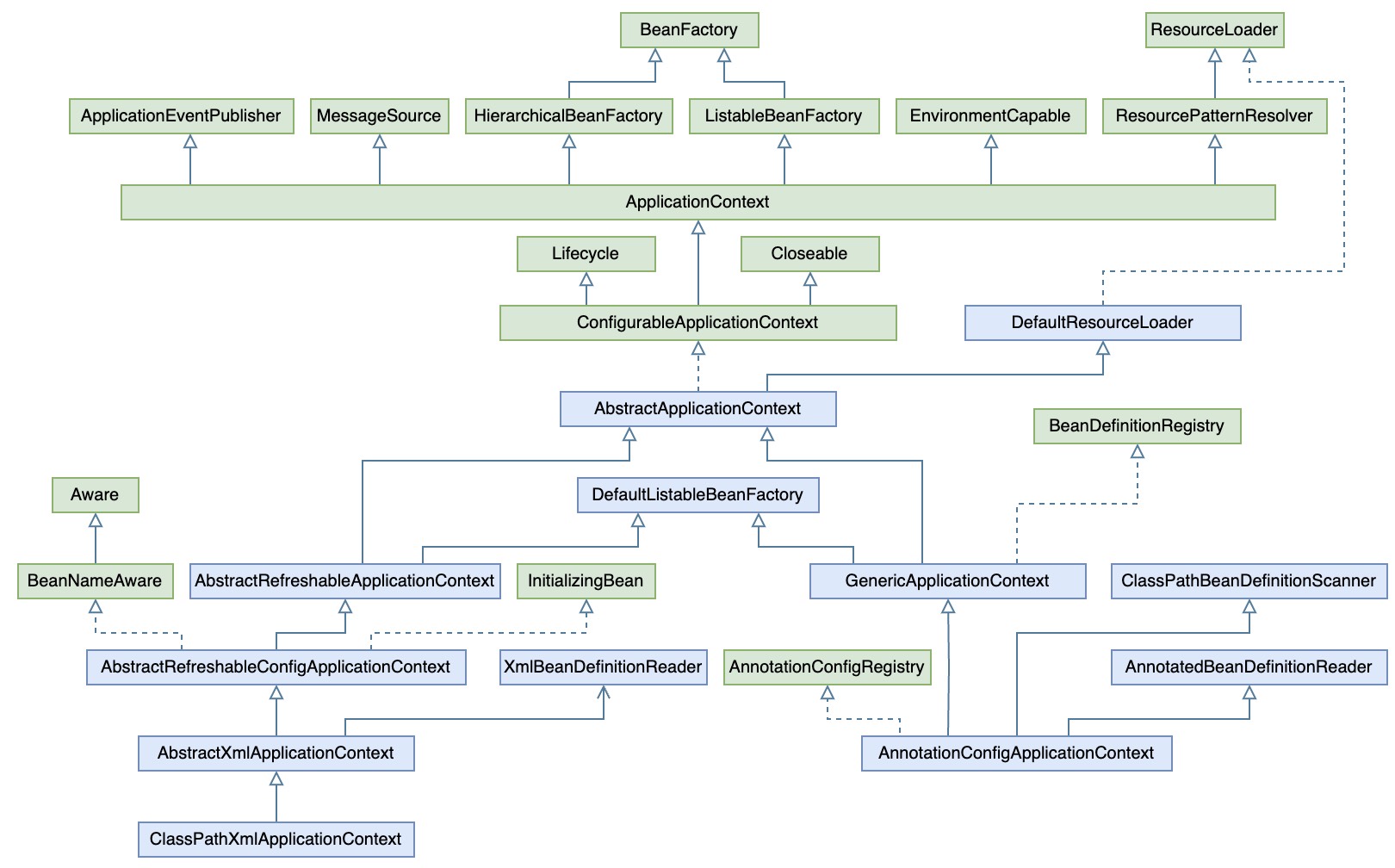
1. AbstractApplicationContext ApplicationContext将上下文定义在其抽象实现AbstractApplicationContext提供的模板方法refresh中,非常清晰,然后分为两个实现分支,即ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,可以画出其相关的类图如下
1.1. refresh 下面梳理一下refresh中几个主要的步骤
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 public void refresh () throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this .startupShutdownMonitor) { prepareRefresh(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); initMessageSource(); initApplicationEventMulticaster(); onRefresh(); registerListeners(); finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); finishRefresh(); }catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } destroyBeans(); cancelRefresh(ex); throw ex; }finally { resetCommonCaches(); } } }
1.1.1. prepareRefresh prepareRefresh主要留给子类做一些操作提前准备操作,比如initPropertySources,用户可以通过继承实现一个自定义的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,然后提前自定义一些property
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 protected void prepareRefresh () { this .startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); this .closed.set(false ); this .active.set(true ); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Refreshing " + this ); }else { logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName()); } } initPropertySources(); getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); this .earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet <>(); }
1.1.2. obtainFreshBeanFactory 这里定义了两个步骤,交给子类实现,要求返回一个准备好的DefaultListableBeanFactory实例化,即完成了BeanDefinition的加载
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory () { refreshBeanFactory(); return getBeanFactory(); }
1.1.3. prepareBeanFactory 对BeanFactory的扩展从这里正式开始,比如添加SPEL语言的支持,添加属性注册编辑器,添加BeanPostProcessor执行Aware操作,以及收集注册ApplicationListener等
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 protected void prepareBeanFactory (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader()); beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver (beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar (this , getEnvironment())); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor (this )); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class); beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this ); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this ); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this ); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector (this )); if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor (beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader (beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties()); } if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment()); } }
1.1.4. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 对于BeanFactoryPostProcessor的具体调用其实委托给了PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate,而这里在具体调用实现中又做了进一步细分,即在调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor之前先调用了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
:org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors ( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet <>(); if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList <>(); List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList <>(); for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); }else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList <>(); String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); boolean reiterate = true ; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false ; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true ; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); }else { invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true , false ); List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList <>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList <>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { }else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); }else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); }else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <>(); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList <>(); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }
1.1.5. initApplicationEventMulticaster 初始化事件广播器ApplicationEventMulticaster,即如果用户没有定义就使用默认的SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,包括内置的和用户定义的
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext mark:11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster () { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { this .applicationEventMulticaster = beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this .applicationEventMulticaster + "]" ); } }else { this .applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster (beanFactory); beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this .applicationEventMulticaster); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " + "[" + this .applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]" ); } } }
1.1.6. registerListeners 初始化完广播器之后,便是向其中注册事件监听器ApplicationListener
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 protected void registerListeners () { for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); } String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true , false ); for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); } Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this .earlyApplicationEvents; this .earlyApplicationEvents = null ; if (earlyEventsToProcess != null ) { for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); } } }
1.1.7. finishBeanFactoryInitialization 最后完成BeanFactory的初始化工作,即设置ConversionService,冻结bean定义,以及提前实例化所有的单例bean,也就是说ApplicationContext在启动时就创建并配置所有的单例bean,这样如果配置中有任何错误也能够立即发现。
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal)); } String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false , false ); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { getBean(weaverAwareName); } beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null ); beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
1.1.8. finishRefresh srping中还提供了Lifecycle接口,实现此接口的bean,spring在启动关闭时会调用其start/stop方法,通常用来配置后台程序,比如启动一直轮询的MQ。finishRefresh中负责对Lifecycle启动的调用,以及分发一些ContextRefreshedEvent事件
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 protected void finishRefresh () { clearResourceCaches(); initLifecycleProcessor(); getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh(); publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent (this )); LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this ); }
2. ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 相对于之前的XmlBeanFactory,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext支持以数组方式加载配置文件,当然这些路径交给了其父类进行保存
:org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext (String configLocation) throws BeansException { this (new String [] {configLocation}, true , null ); } public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ( String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super (parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } }
2.1. obtainFreshBeanFactory 有了配置文件之后,再看其如何初始化BeanFactory,即对obtainFreshBeanFactory的实现
具体分成了两步,首先刷新,如果已经存在则销毁,然后创建一个新的
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext mark:10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected final void refreshBeanFactory () throws BeansException { if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this .beanFactoryMonitor) { this .beanFactory = beanFactory; } }catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException ("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
至于其中对BeanDefinitions的加载还是委托给了XmlBeanDefinitionReader,前面已经有过详细介绍,不再赘述,事实上到这里,就已经覆盖了前面BeanFactory提供的全部功能,剩下的就是如何在这个基础上做一些扩展了
:org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 protected void loadBeanDefinitions (DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader (beanFactory); beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this .getEnvironment()); beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this ); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver (this )); initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
示例 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 这里还是复用之前的示例,除了多添加一个依赖spring-context,不需要其它修改
:pom.xml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-core</artifactId > <version > 5.1.3.RELEASE</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-beans</artifactId > <version > 5.1.3.RELEASE</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-context</artifactId > <version > 5.1.3.RELEASE</version > </dependency >
然后便可以直接使用了,只是有个区别,之前的bean是在调用getBean时才加载,而这里是在ApplicationContext初始化时就进行加载
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class App { public static void main (String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("bean.xml" ); User user = (User)context.getBean("test" ); System.out.println(user.getName() + ":" + user.getEmail()); } }
3. AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 除了在配置文件中定义BeanDefinition,spring同时支持注解的方式AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,以及直接手动注入的方式GenericApplicationContext,下面看下基于注解的实现
首先它构造中初始化了AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader和ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,同时在父类中初始化了DefaultListableBeanFactory,如果指定了扫描路径,则直接进行BeanDefinition的扫描注册,并初始化上下文
:org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext () { this .reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader (this ); this .scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner (this ); } public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (String... basePackages) { this (); scan(basePackages); refresh(); }
3.1. ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
委托父类进行BeanDefinition的加载和过滤
对过滤后的BeanDefinition进行一些简单的处理,比如默认属性填充,然后注册
:org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner mark:4,18,33 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public int scan (String... basePackages) { int beanCountAtScanStart = this .registry.getBeanDefinitionCount(); doScan(basePackages); if (this .includeAnnotationConfig) { AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this .registry); } return (this .registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart); } protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan (String... basePackages) { Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified" ); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet <>(); for (String basePackage : basePackages) { Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage); for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) { ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this .scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate); candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName()); String beanName = this .beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this .registry); if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName); } if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate); } if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder (candidate, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this .registry); beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder); registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this .registry); } } } return beanDefinitions; }
父类ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider中的逻辑:
查看构造器会发现,默认注册的过滤器只有一个,即includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));,也就是说上下文启动时,默认会加载@Component,以及使用@Component标识了的@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Configuration,另外还对注解@Conditional做了处理,即是否忽略
默认的过滤条件:首先要是独立的,即如果实例化不需要依赖别的类,比如内部非静态类就不行,其次要是具体的实现类,或者如果是抽象类但是指定了look-up也行
:org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider mark:9,18,27,28,29,36 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 private final List<TypeFilter> includeFilters = new LinkedList <>();private final List<TypeFilter> excludeFilters = new LinkedList <>();public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents (String basePackage) { if (this .componentsIndex != null && indexSupportsIncludeFilters()) { return addCandidateComponentsFromIndex(this .componentsIndex, basePackage); }else { return scanCandidateComponents(basePackage); } } private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents (String basePackage) { Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet <>(); try { String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this .resourcePattern; Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath); boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled(); boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled(); for (Resource resource : resources) { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Scanning " + resource); } if (resource.isReadable()) { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource); if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) { ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition (metadataReader); sbd.setResource(resource); sbd.setSource(resource); if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource); } candidates.add(sbd); }else { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource); } } }else { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource); } } }catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException ( "Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex); } }else { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource); } } } }catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException ("I/O failure during classpath scanning" , ex); } return candidates; } protected boolean isCandidateComponent (MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException { for (TypeFilter tf : this .excludeFilters) { if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) { return false ; } } for (TypeFilter tf : this .includeFilters) { if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) { return isConditionMatch(metadataReader); } } return false ; } protected boolean isCandidateComponent (AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) { AnnotationMetadata metadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata(); return (metadata.isIndependent() && (metadata.isConcrete() || (metadata.isAbstract() && metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Lookup.class.getName())))); }
对于@Conditional注解的处理如下,注解中可以写多个Condition条件,进行与运算,并且spring将对应class的元数据,以及整个容器和环境变量都交给了调用者,以防其在判断中需要
:org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap.ConditionEvaluator 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public boolean shouldSkip (@Nullable AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, @Nullable ConfigurationPhase phase) { if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) { return false ; } if (phase == null ) { if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata && ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate((AnnotationMetadata) metadata)) { return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION); } return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN); } List<Condition> conditions = new ArrayList <>(); for (String[] conditionClasses : getConditionClasses(metadata)) { for (String conditionClass : conditionClasses) { Condition condition = getCondition(conditionClass, this .context.getClassLoader()); conditions.add(condition); } } AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(conditions); for (Condition condition : conditions) { ConfigurationPhase requiredPhase = null ; if (condition instanceof ConfigurationCondition) { requiredPhase = ((ConfigurationCondition) condition).getConfigurationPhase(); } if ((requiredPhase == null || requiredPhase == phase) && !condition.matches(this .context, metadata)) { return true ; } } return false ; }
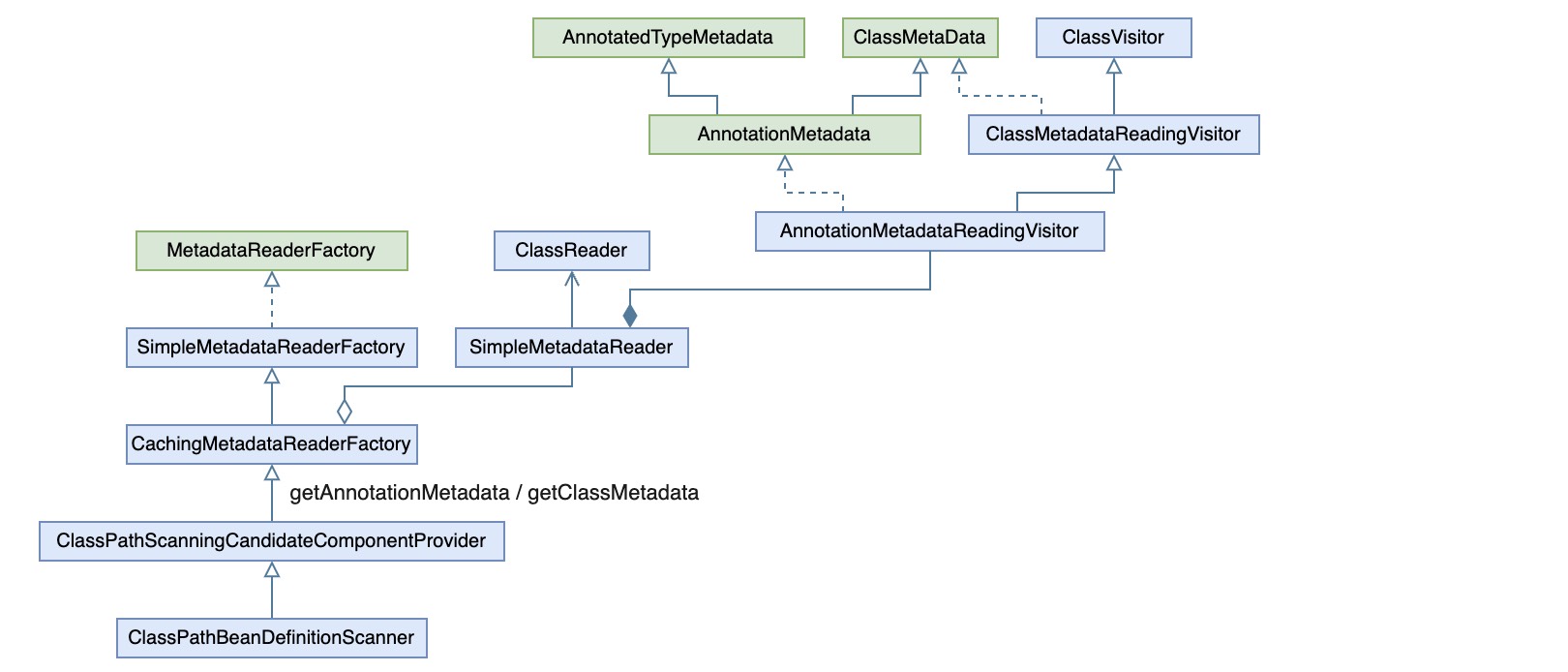
其实这里比较关键的是借助了ASM对所有的class进行读取,并统一封装成AnnotationMetadata,这里首先保证了读取后是一个全集,这是后面能实现注解驱动的基础,至于实现则封装在SimpleMetadataReader的构造器中,实际上最终将读取的任务委托给了ClassReader,而使用ClassReader读取需要给定ClassVisitor,因此AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor继承自了ClassVisitor,可以画出它们之间的类图关系:
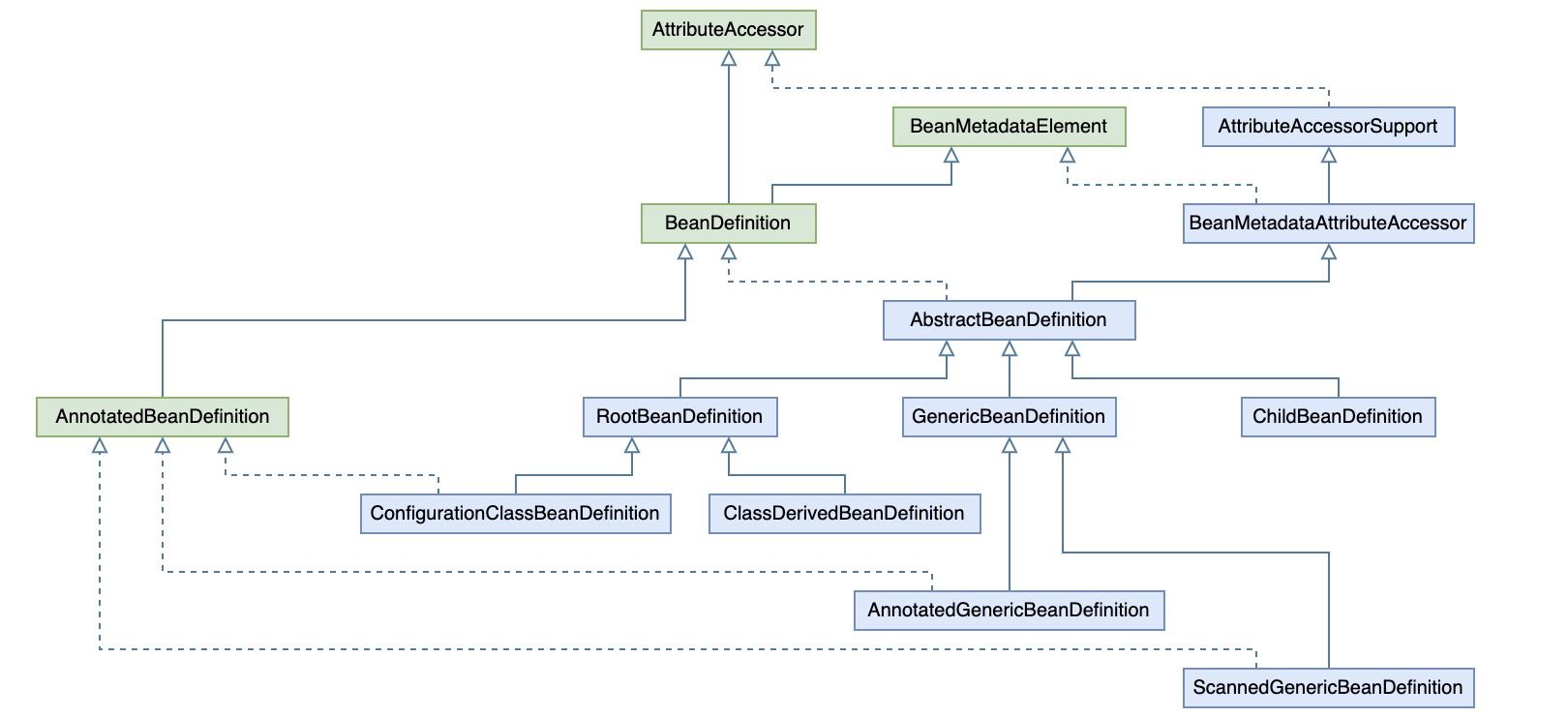
另外这里对过滤后的结果包装成ScannedGenericBeanDefinition,即用BeanDefinition封装了上面的AnnotationMetadata
示例 @Component 了解了spring的套路之后,可以定义一个自己@Component,并定义一个BeanPostProcessor进行一些自定义的代理操作
:SelfComponent.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Component public @interface SelfComponent { @AliasFor(annotation = Component.class) String value () default "" ; }
:SelfProxy.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public class SelfProxy implements MethodInterceptor { @Override public Object intercept (Object object, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { before(object, method, args); Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(object, args); after(object, method, args); return result; } private void before (Object object, Method method, Object[] objects) { System.out.println("before " + method.getName() + "..." ); } private void after (Object object, Method method, Object[] objects) { System.out.println("after " + method.getName() + "..." ); } }
:SelfBeanPostProcessor.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Component public class SelfBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Class<?> beanClass = bean.getClass(); if (beanClass.isAnnotationPresent(SelfComponent.class)){ Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer (); enhancer.setSuperclass(beanClass); enhancer.setCallback(new SelfProxy ()); return enhancer.create(); } return bean; } }
:User.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @SelfComponent public class User { private String name = "shanhm1991" ; private String email = "shanhm1991@163.com" ; public String getName () { return name; } public String getEmail () { return email; } }
:App.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class App { public static void main (String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ("test.test" ); User user = (User)context.getBean("user" ); System.out.println(user.getName() + ":" + user.getEmail()); } } before getName... after getName... before getEmail... after getEmail... shanhm1991:shanhm1991@163. com
3.2. AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader负责对上面注册的BeanDefinition进行处理,但是初始化之后没有看到任何地方对其进行任何调用,其实它是在构造器中注册了一堆BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,并将具体的事情分给了这些processor去处理
:org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader mark:6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader (BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null" ); Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null" ); this .registry = registry; this .conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator (registry, environment, null ); AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this .registry); }
:org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils mark:17 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors ( BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry); if (beanFactory != null ) { if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) { beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE); } if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) { beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver ()); } } Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet <>(8 ); if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition (ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition (AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition (CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition (); try { def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader())); }catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException ( "Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex); } def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition (EventListenerMethodProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition (DefaultEventListenerFactory.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)); } return beanDefs; }
3.2.1. ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 这里不打算对所有的processor进行分析,但有必要看下ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的实现,因为它是后面很多功能实现的基础
根据它实现的接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,从上面1.1.4的分析可以知道,入口就是下面两个方法
3.2.1.1. postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
委托ConfigurationClassUtils过滤出所有配置类的BeanDefinition
委托ConfigurationClassParser对配置类上各种注解信息进行解析parse,解析ConfigClass,并递归处理
委托ConfigurationClassParser对解析的ConfigClass进行校验validate
委托ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader依次对ConfigClass进行再解析,主要是一些记录的信息还没有转换成对应的BeanDefinition以及注册,比如@Bean方法以及ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的实现
:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor mark:13,53,54,65 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 public void processConfigBeanDefinitions (BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList <>(); String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String beanName : candidateNames) { BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef); } }else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this .metadataReaderFactory)) { configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder (beanDef, beanName)); } } if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) { return ; } configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> { int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition()); int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition()); return Integer.compare(i1, i2); }); SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null ; if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) { sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry; if (!this .localBeanNameGeneratorSet) { BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR); if (generator != null ) { this .componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator; this .importBeanNameGenerator = generator; } } } if (this .environment == null ) { this .environment = new StandardEnvironment (); } ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser ( this .metadataReaderFactory, this .problemReporter, this .environment, this .resourceLoader, this .componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet <>(configCandidates); Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet <>(configCandidates.size()); do { parser.parse(candidates); parser.validate(); Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet <>(parser.getConfigurationClasses()); configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed); if (this .reader == null ) { this .reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader ( registry, this .sourceExtractor, this .resourceLoader, this .environment, this .importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry()); } this .reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses); alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses); candidates.clear(); if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) { String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet <>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames)); Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet <>(); for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) { alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); } for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) { if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) { BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this .metadataReaderFactory) && !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) { candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder (bd, candidateName)); } } } candidateNames = newCandidateNames; } }while (!candidates.isEmpty()); if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) { sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry()); } if (this .metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) { ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this .metadataReaderFactory).clearCache(); } }
3.2.1.1.1 checkConfigurationClassCandidate
从BeanDefinition中获取AnnotationMetadata
上面注册的ScannedGenericBeanDefinition已经填充过了,如果获取不到,再直接通过ASM读取一次
:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassUtils mark:41,44 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 private static final Set<String> candidateIndicators = new HashSet <>(8 );static { candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName()); candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName()); candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName()); candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName()); } public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate (BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) { String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName(); if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null ) { return false ; } AnnotationMetadata metadata; if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition && className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) { metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata(); }else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) { Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass(); metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata (beanClass, true ); }else { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className); metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); }catch (IOException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " + className, ex); } return false ; } } if (isFullConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL); }else if (isLiteConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE); }else { return false ; } Integer order = getOrder(metadata); if (order != null ) { beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order); } return true ; } public static boolean isFullConfigurationCandidate (AnnotationMetadata metadata) { return metadata.isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName()); } public static boolean isLiteConfigurationCandidate (AnnotationMetadata metadata) { if (metadata.isInterface()) { return false ; } for (String indicator : candidateIndicators) { if (metadata.isAnnotated(indicator)) { return true ; } } try { return metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName()); }catch (Throwable ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to introspect @Bean methods on class [" + metadata.getClassName() + "]: " + ex); } return false ; } }
3.2.1.1.2 parse
包括@PropertySource、@ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource、@Bean,下面主要看下对@Import的解析
其实就是将@Import注解指定的class识别成配置类,并注册到容器中,这里分了三种情况:
如果指定的class实现了ImportSelector,则获取其实现类中返回的class,另外这里还在做了细分,就是如果进一步实现了DeferredImportSelector,则放到最后处理,并按照顺序
如果指定的class实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,则先记到ConfigurationClass中,后面处理
如果是一个普通类,就把成一个配置类处理
递归处理父类,直至父类是java包中的类或者已经处理过
:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser mark:25,48,98,146,161,171 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 public void parse (Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) { for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) { BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition(); try { if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName()); }else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) { parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName()); }else { parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } }catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; }catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException ( "Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]" , ex); } } this .deferredImportSelectorHandler.process(); } protected void processConfigurationClass (ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException { if (this .conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) { return ; } ConfigurationClass existingClass = this .configurationClasses.get(configClass); if (existingClass != null ) { if (configClass.isImported()) { if (existingClass.isImported()) { existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass); } return ; }else { this .configurationClasses.remove(configClass); this .knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals); } } SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass); do { sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass); }while (sourceClass != null ); this .configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass); } protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass (ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException { if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) { processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass); } for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class, org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) { if (this .environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) { processPropertySource(propertySource); }else { logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment" ); } } Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class); if (!componentScans.isEmpty() && !this .conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) { for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) { Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions = this .componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) { BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); if (bdCand == null ) { bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition(); } if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this .metadataReaderFactory)) { parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } } } processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true ); AnnotationAttributes importResource = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class); if (importResource != null ) { String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations" ); Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader > readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader" ); for (String resource : resources) { String resolvedResource = this .environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource); configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass); } } Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass); for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) { configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod (methodMetadata, configClass)); } processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass); if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) { String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName(); if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java" ) && !this .knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) { this .knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass); return sourceClass.getSuperClass(); } } return null ; } private void processImports (ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass, Collection<SourceClass> importCandidates, boolean checkForCircularImports) { if (importCandidates.isEmpty()) { return ; } if (checkForCircularImports && isChainedImportOnStack(configClass)) { this .problemReporter.error(new CircularImportProblem (configClass, this .importStack)); }else { this .importStack.push(configClass); try { for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) { if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) { Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass(); ImportSelector selector = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class); ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods( selector, this .environment, this .resourceLoader, this .registry); if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) { this .deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector); }else { String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata()); Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames); processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, false ); } }else if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)) { Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass(); ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar registrar = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class); ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods( registrar, this .environment, this .resourceLoader, this .registry); configClass.addImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(registrar, currentSourceClass.getMetadata()); }else { this .importStack.registerImport( currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName()); processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass)); } } }catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; }catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException ( "Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" + configClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]" , ex); }finally { this .importStack.pop(); } } }
3.2.1.1.3 validate ConfigurationClassParser并没有自己进行校验逻辑处理,而是具体的校验工作交给了被校验者自己,只要最后将校验结果告诉ConfigurationClassParser就行了,这样设计使得分工更明确
Configuration类的校验,主要是配置类不可以是final
:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClass 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public void validate (ProblemReporter problemReporter) { if (getMetadata().isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName())) { if (getMetadata().isFinal()) { problemReporter.error(new FinalConfigurationProblem ()); } } for (BeanMethod beanMethod : this .beanMethods) { beanMethod.validate(problemReporter); } }
Bean方法的校验:如果是静态方法则直接通过,否则如果类是Configuration,则方法不能是final的
:org.springframework.context.annotation.BeanMethod 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void validate (ProblemReporter problemReporter) { if (getMetadata().isStatic()) { return ; } if (this .configurationClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName())) { if (!getMetadata().isOverridable()) { problemReporter.error(new NonOverridableMethodError ()); } } }
3.2.1.1.4 loadBeanDefinitions 这里要说一下ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,除了上面根据ImportSelector来指定要注册的配置类之外,spring还可以直接将整个注册操作交给我们来定义,并且会将对应类的元信息,以及注册器交给我们使用
:org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader mark:21 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass ( ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) { if (trackedConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass)) { String beanName = configClass.getBeanName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this .registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { this .registry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName); } this .importRegistry.removeImportingClass(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); return ; } if (configClass.isImported()) { registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass); } for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) { loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod); } loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources()); loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars()); } private void loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars (Map<ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, AnnotationMetadata> registrars) { registrars.forEach((registrar, metadata) -> registrar.registerBeanDefinitions(metadata, this .registry)); }
示例 @Import ImportSelector就不说了,这里说一个ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar在实际开发中非常有用的场景:将指定路径下的标识了指定注解的类注册到spring容器中
首先定义一个自定义注解,并用@Import标识,所以它也是一个@Import,与上面的@Component同理
:TestScan.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Documented @Import(TestRegistrar.class) public @interface TestScan { String[] basePackages(); }
然后在目标类上进行标识,这个类要能通过spring的扫描过滤,不一定非要@Configuration
:ImportConfigurationBean.java 1 2 3 4 5 @Component @TestScan(basePackages="test.aop") public class ImportConfigurationBean { }
定义实现,作为示例这里路径简单获取了下并没有真正使用
:TestRegistrar.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class TestRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions (AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { Map<String, Object> map = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(TestScan.class.getName()); System.out.println("获取到注解中的信息" + map); GenericBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition (); beanDefinition.setBeanClass(ImportedBean.class); registry.registerBeanDefinition("importedBean" , beanDefinition); } }
:ImportedBean.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 public class ImportedBean { public void hello () { System.out.println("hello shanhm." ); } }
:App.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class App { public static void main (String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ("test.aop" ); context.getBean(ImportedBean.class).hello();; } }
参考:
《spring源码深度解析》 郝佳
https://blog.csdn.net/andy_zhang2007/article/details/78549773